In industrial manufacturing, the comparison between closed die vs open die forging is rarely theoretical. It usually starts with a real question: Can this part meet performance and tolerance requirements without unnecessary cost or risk? Understanding how these two forging methods behave in actual production environments is essential for making the right technical and commercial decision.
Rather than viewing them as competing processes, closed die and open die forging should be understood as complementary solutions designed for different manufacturing priorities.
Closed Die vs Open Die Forging Based on Shape Control and Metal Flow
One of the most practical ways to evaluate closed die vs open die forging is by looking at how metal flow is controlled during deformation.
In open die forging, the material is only partially constrained. The metal flows outward under compressive force, and the final shape is gradually achieved through multiple forging passes. This makes open die forging adaptable, especially for large or non-standard geometries.
Closed die forging works differently. The material is guided into a defined cavity, forcing the metal to follow a predetermined path. This controlled flow is what allows closed die forging parts to maintain consistent geometry and predictable internal structure from one batch to the next.
Closed Die vs Open Die Forging in Mechanical Performance Requirements
When load-bearing performance is critical, the distinction between closed die vs open die forging becomes more pronounced.
Open die forging produces sound internal structure and is well suited for components subjected to static or moderate loads. However, dimensional variation and grain flow orientation depend heavily on process control.
Closed die forging, including closed die hot forging, aligns grain flow with the functional shape of the part. This results in improved fatigue resistance, higher strength-to-weight ratios, and more reliable performance under cyclic loading. These characteristics explain why closed die forging applications are common in automotive, oil & gas, and aerospace systems.
Benefits of Closed Die Forging Over Open Die Forging
In terms of production, the advantages of closed die forging are obvious especially if consistency and efficiency are important factors. Closed die drop forging enables manufacturing of components that are to a great extent net-shape thus drastically cutting down on the amount of machining that comes after.
Open die forging provides the advantage of flexibility and with a lesser investment on tooling, however, closed die forging factories usually have better repeatability and can hold tighter tolerances. When the production volume is medium to high this is frequently reflected in a lower total cost of manufacturing even if the initial die expenditure is higher.
Closed Die vs Open Die Forging Products and Typical Use Cases
The kind of products that are made through closed die vs open die forging is a mirror of the different strong points of the two processes.
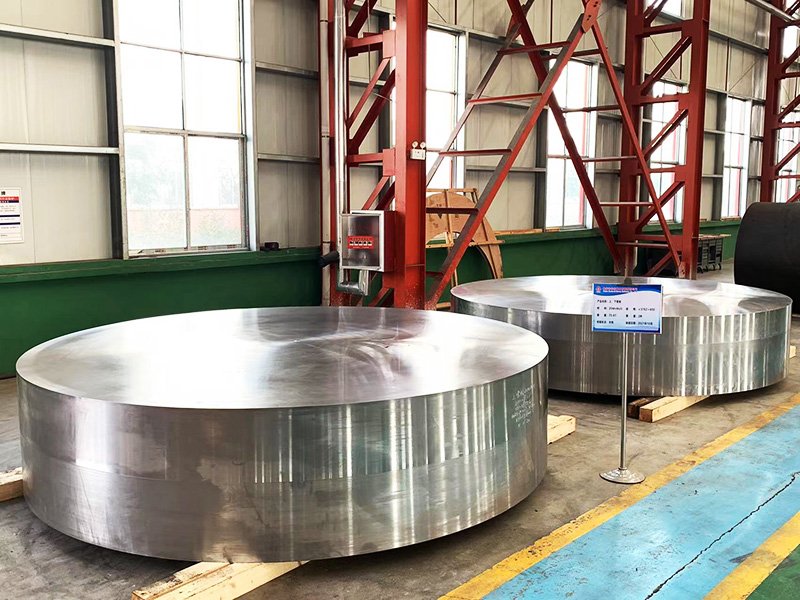
Open die forging is mainly done for large shafts, rings, and blocks where the emphasis is on the size and customization.
Closed die forging products are generally the precision components such as forged flanges, valve bodies, hubs, fittings, and structural parts. These closed die forging components are made in such a way that they can be used directly in assemblies where the requirements for dimensional accuracy and interchangeability are quite high.



Closed Die vs Open Die Forging in Aerospace and High-Spec Industries
Decisions on metal closed die forging for aerospace are very much affected by the strict requirements for performance and traceability. Closed die forging is preferred since it gives you uniform mechanical properties and consistent quality that can be repeated over production runs.
By and large, open die forging might still be utilized for big preforms, however, the final aerospace components most often depend on closed die forging to meet the criteria of strength, weight optimization, and certification standards.
Closed Die vs Open Die Forging: Hot, Cold, and Press Forging Considerations
The majority of industrial analyses that look at both closed die and open die forging are concentrated on hot forging where the ability of the material to be ductile is just the right attribute for complex shapes to be formed with high efficiency. Closed die hot forging is still the prevalent mode for the production of steel and alloy parts.
In certain applications, cold closed die forging is applied to smaller parts where surface finish and dimensional precision outweigh forming force requirements. Closed die forging may also be performed using press systems rather than hammers, providing controlled deformation and improved internal consistency for demanding materials.
Closed Die Forging Services Provided by TIP TOP Forging
As a professional manufacturer, TIP TOP Forging offers both open die and closed die forging services, supporting customers across multiple industries. Our closed die forging capabilities cover carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and selected nickel-based materials.
Typical closed die forging products from TIP TOP Forging include forged blocks, flanges, valve bodies, hubs, stepped shafts, and custom-engineered components. By combining closed die press forging and hammer forging processes, we adapt the manufacturing route to the functional requirements of each part.



Closed Die vs Open Die Forging from a Cost and Volume Perspective
Another practical way to assess closed die vs open die forging is through production volume.Open-die forging can be a very economical choice for small runs or very large parts since it requires very little tooling.
Closed-die forging on the other hand makes use of dies that are a one-time investment, but the cost of these can be easily recovered when the number of parts is increased or the consistency of the part, which is achieved by the closed-die process, allows risk of the assembly and inspection costs to be lowered. For a lot of industrial purchasers, closed-die forging services give better long-term value even though there is a higher initial tooling expense.
Summary: Making Practical Decisions Between Closed Die and Open Die Forging
You cannot find a one-size-fits-all answer for the closed die vs open die forging comparison. The right answer depends very much on the shape of the part, the level of performance required, how tight the tolerances are going to be, and the size of the production run. Open die forging is mostly known for its flexibility and quite literally unlimited size capability whereas closed die forging is known for its precision, repeatability as well as the highest level of mechanically performance.
TIP TOP Forging is a company with extensive experience in closed die forgings. By knowing the differences and reaching out to such a company, manufacturers can make a choice of the forging method that is the best fit for their both technically and financially needs.
