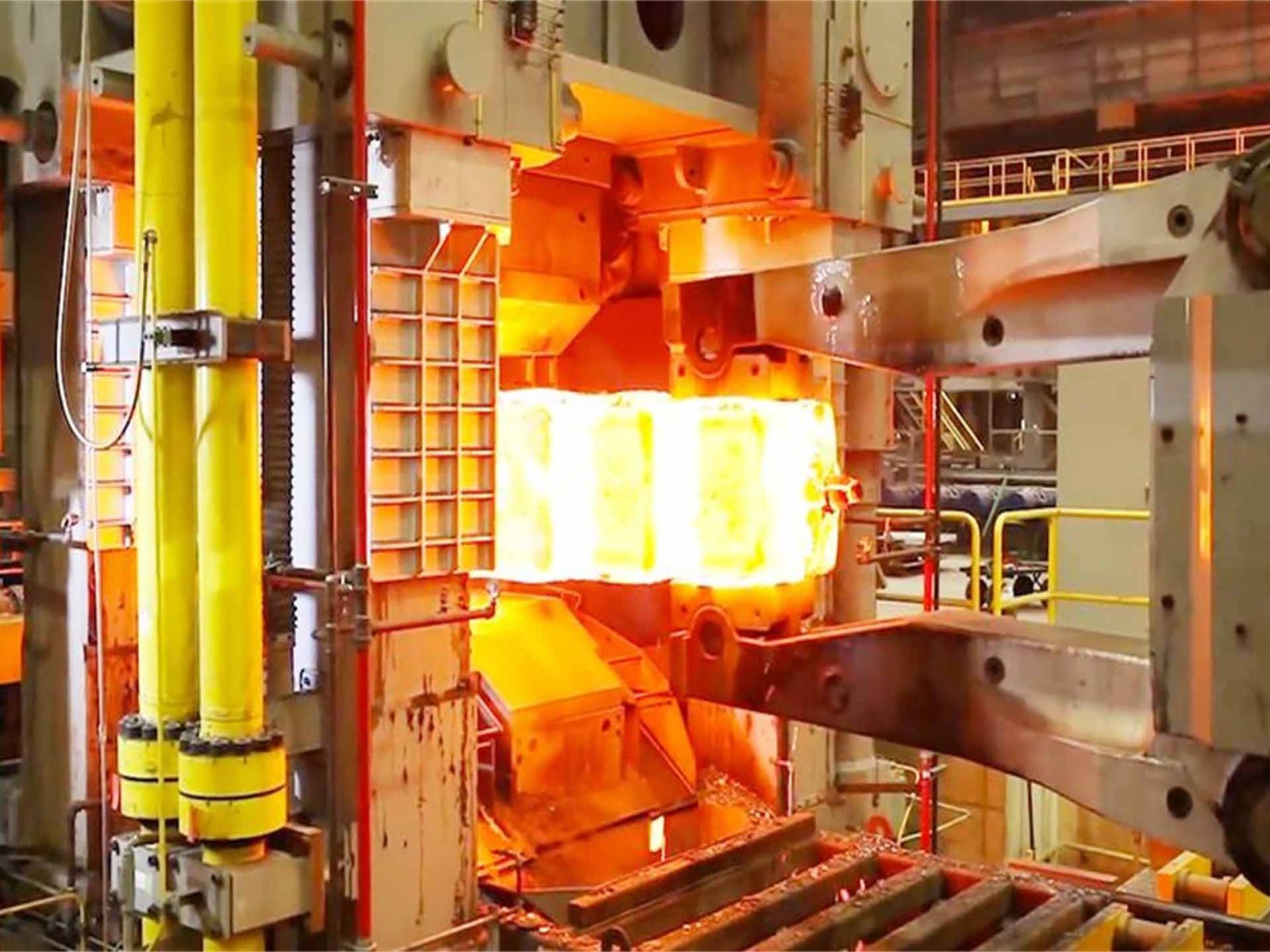
What Is Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging
What is open die forging and closed die forging refers to two fundamentally different metal forming methods used to shape heated metal through compressive force. In open die forging and closed die forging, the key difference lies in whether the dies fully enclose the workpiece during deformation.
Open die forging uses flat or simple dies that allow the material to flow freely, while closed die forging employs shaped dies that define the final geometry. Both processes are widely used in industrial manufacturing, but each serves different production requirements.
Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging Process Overview
The open and closed die forging process begins by heating the metal to a suitable forging temperature. In open die forging, the material is compressed between open dies using a forging press or hammer, allowing gradual shaping through multiple strokes.
In closed die forging, the heated billet is placed into a die cavity and deformed until it fills the impression. This open die forging and closed die forging process distinction directly affects part size, tooling cost, and dimensional accuracy.
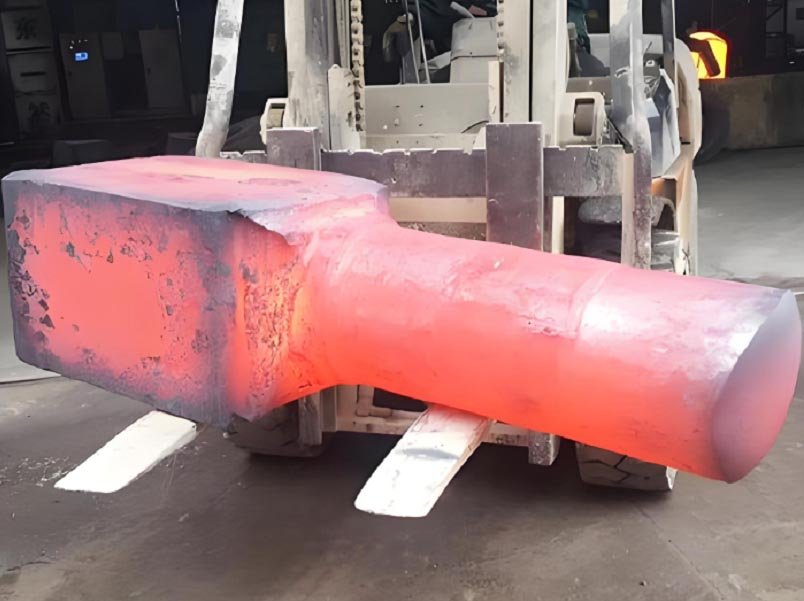
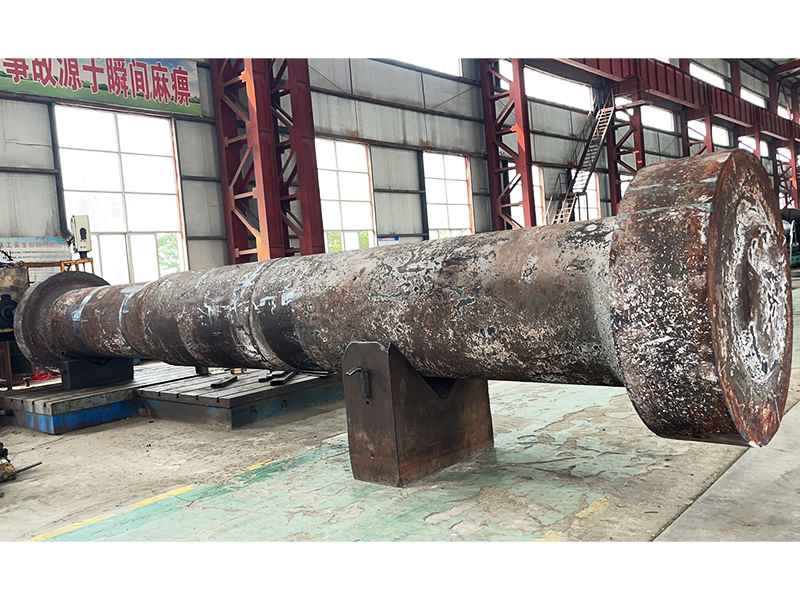
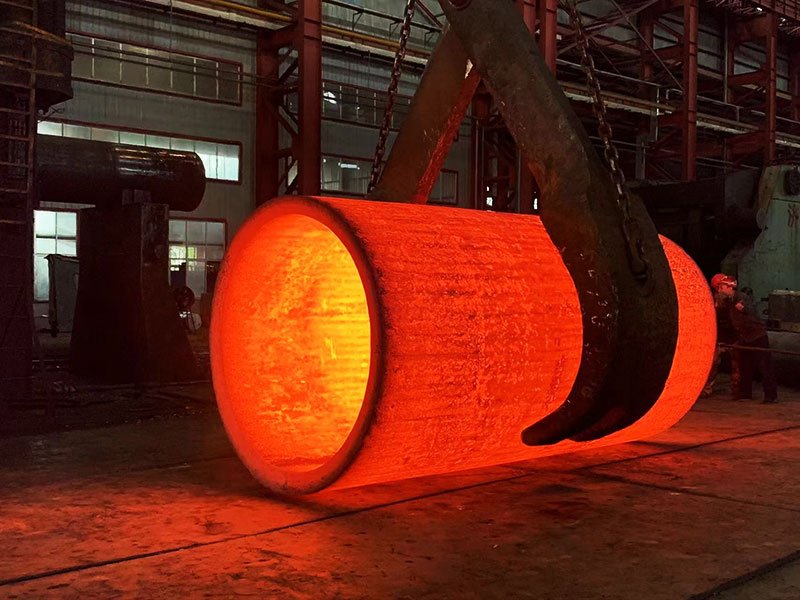



Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging Diagram Explanation
An open die forging diagram typically shows a workpiece being compressed between flat dies, with material flowing outward in a controlled manner. This visual highlights the flexibility of open die forging, especially for large cross-sections.
By contrast, a closed die forging diagram illustrates the metal being forced into a shaped cavity, where excess material forms flash. Comparing an open die forging and closed die forging diagram helps buyers understand material flow, deformation control, and tooling limitations.
Differentiate Between Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging
To differentiate between open die forging and closed die forging, several factors must be considered. Open die forging supports large and customized parts with excellent internal quality, while closed die forging excels in producing smaller, complex shapes with high repeatability.
Open die forging typically requires more machining after forging, whereas closed die forging produces near-net shapes. These distinctions are critical when selecting the appropriate forging method.
Open Die Forging Advantages and Disadvantages Compared to Closed Die Forging
When evaluating open die forging advantages and disadvantages within open die forging and closed die forging, open die forging offers superior grain structure, lower tooling costs, and virtually unlimited part size. These advantages make it ideal for large forged components.
However, open die forging may result in looser dimensional tolerances and higher machining requirements. Closed die forging provides better surface definition but comes with higher die costs and size limitations.
Advantages of Open Die Forging Process for Large Components
The advantages of open die forging process become particularly clear in the production of large and heavy parts. Open die forging enables deep deformation penetration, refined grain flow, and elimination of internal defects across thick sections.
Compared with closed die forging, open die forging is better suited for low-volume, high-value components where mechanical performance is prioritized over cosmetic accuracy.
Open Die Forging Press and Open Die Press Forging Equipment
Open die forging and closed die forging rely on different equipment configurations. Open die forging press systems are typically hydraulic presses capable of delivering high tonnage for large-scale deformation. Open die press forging allows precise control of deformation speed and force.
Closed die forging often uses mechanical or hydraulic presses with dedicated dies designed for specific part geometries. Equipment selection directly impacts production efficiency and part capability.
Open Die Cold Forging and Closed Die Forging Considerations
Although most open die forging and closed die forging operations are performed hot, open die cold forging may be used for limited size components where surface finish and dimensional control are critical. Cold forging requires significantly higher forces and is less common for large sections.
Closed die forging is more adaptable to cold or warm forging conditions for smaller parts, depending on material and application requirements.
Applications of Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging
Open die forging and closed die forging are applied across different industrial needs. Open die forging is commonly used for large shafts, rings, blocks, cylinders, and pressure components that require superior internal quality.
Closed die forging is widely applied for smaller, high-volume components where precise geometry and repeatability are essential. Understanding application differences helps manufacturers and buyers select the correct process.
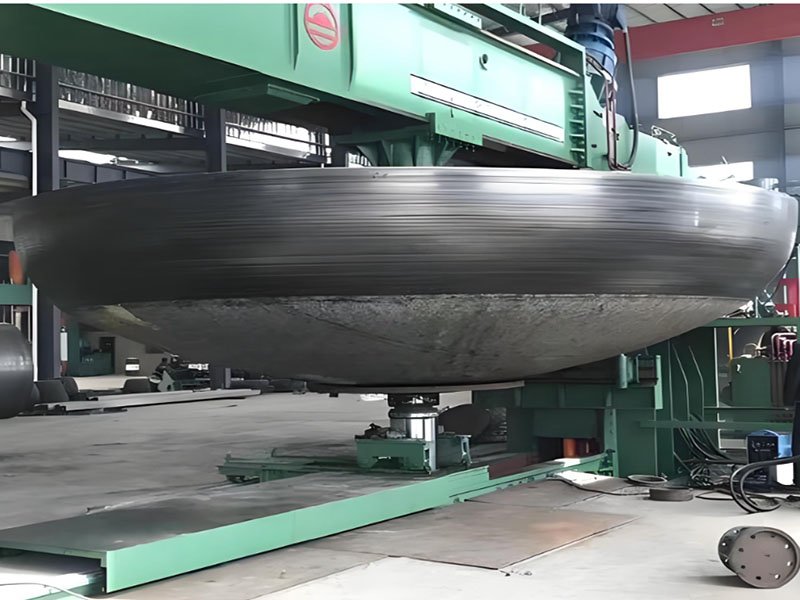
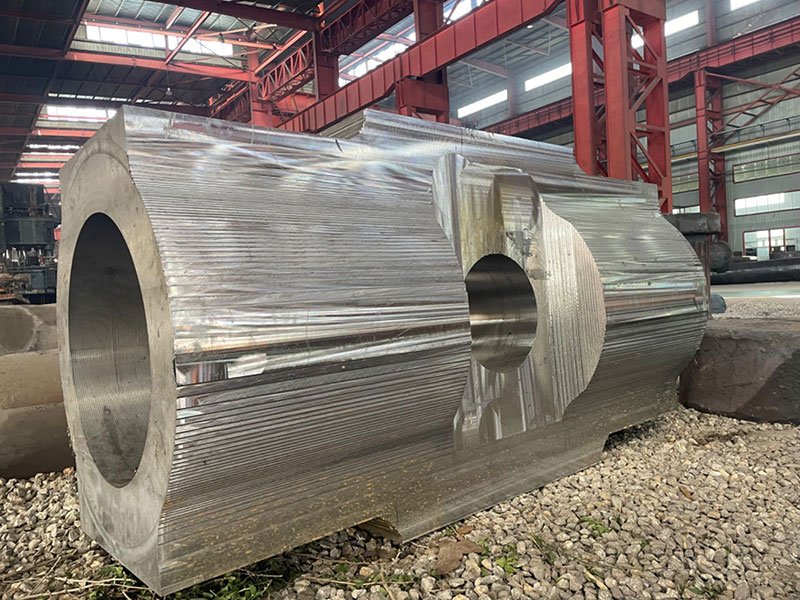
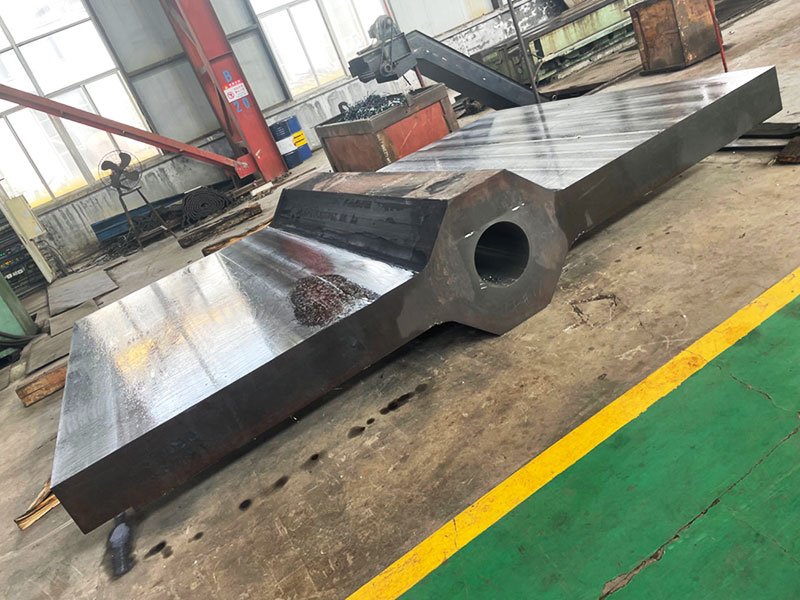



TIP TOP Expertise in Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging
TIP TOP Forging specializes in open die forging and closed die forging, with a strong focus on large open die forged components. Our facilities are equipped with high-capacity forging presses, controlled heat treatment systems, and comprehensive inspection capabilities.
We support customers by selecting the appropriate open die forging and closed die forging process based on part size, mechanical requirements, and production volume. TIP TOP delivers forged components with consistent quality, reliable performance, and full material traceability.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Open Die Forging and Closed Die Forging
Choosing between open die forging and closed die forging depends on part size, complexity, quantity, and performance requirements. Open die forging is the preferred solution for large, heavy, and customized components, while closed die forging is suitable for smaller, high-volume parts.
By working with an experienced forging manufacturer like TIP TOP, customers can confidently select the most appropriate forging process to meet both technical and commercial objectives.
